13 Types of Fats and Oils used in Hotels and Restaurants
The oils and fats used in the kitchen are extracted in some manner from plants and animals. The methods used affect the quality of the product and how they can be used in cooking.
OilSeveral kinds of oil are used to make salad dressing;e.g. olive; peanut; sunflower; walnut; grape se... is a fatty substance that is liquid at normal or room temperature. Oils and fats used for cooking are extracted from fruit (Olive), seeds (canola, Sunflower), grains (corn), legumes (peanut), nuts (walnuts), and other sources.
The Egyptians made the oldest use of oil and they used the sesame oil. In Greece, the olive tree was a sacred tree and a symbol of the city of Athens. Oil was not only for food but also used as a fuel to provide light and heat for many centuries.
What is the Definition of fats and oils?
- Fats can be defined as a soft greasy substance found in organic tissue.
- The function of fat is to protect the vital organs of the body, to provide heat and energy and certain fats provide vitamins.
- Fats can be divided into solid fats and oils.
- Fats are a cooking medium.
- Fats were traditionally of animal origin.
- The quality of solidifying naturally distinguishes saturated fats and unsaturated fats like vegetable oils.
- They are the chief source of energy.
Other Interesting facts about oils and fats:
Pure oils are taken from a single vegetable species. Whereas the term vegetable oil indicates that they are a blend of two or more vegetable oils. Most oils sold today are refined oils, which means that during processing, their original taste and flavor have been removed.
However, there are still a few oils, which are processed by cold pressing and are termed virgin or natural oils as they still retain the taste of their vegetable origins. (E.g. Olive oil)
- Used in marinades for vegetables, meats, seafood, kebabs, etc.
- Preservatives: Used in preserving Indian pickles, and also to preserve goats’ cheese, meats, fish, and herbs.
- Used to make sauces: MayonnaiseThick cold basic sauce made of egg yolks; oil and vinegar; for serving with cold eggs; fish; vegetab..., aioli, pesto, etc.
- Used as an ingredient in cold dressings: VinaigretteSalad-dressing; a sauce made of oil; vinegar and seasonings..
- Used directly in most of the basic principles of cookery like deep frying, shallow frying, sautéing, braising, searing, etc.,
1. BUTTER

- Butter is the finest fat available in terms of flavor, mouthfeel, and richness.
- Even though there is nothing that can duplicate the taste of butter some people prefer margarine.
- Butter is normally 81% milkfat, 01% milk solids, 1.5 to 2.0% salt, and 16% water.
- High-quality butter will be creamy and without any grains.
2. MARGARINE

- Margarine is made from vegetable oils.
- Contains milk animal fats or fish oils, plus emulsifiers and coloring agents.
- Oils are hydrogenated to form solids.
- Its characteristics are similar to butter.
- It is not suitable for frying.
- Too soft to be rubbed into flour.
3. SUET

- Comes from the Latin word tallow.
- Was used instead of wax for making candles.
- It is stiff and melts slowly.
- It is firm white fat and surrounds lamb or ox’s kidneys.
- Used for sweet puddings such as Christmas pudding, and jam roly-poly.
- Used in savory ones like steak and kidney and steaks and mushrooms.
- When mixed with flour it is one of the most satisfying winter foods.
4.LARD

- LardLard - The soft; white; solid or semi-solid fat rendered from the fatty tissue of the hog. is pork fat.
- Light and clean tasting.
- Mainly used for frying.
- Also used in the bakery because of its creaming properties.
- The best lards are the ones rendered from the belly fat or the bacon big.
- And from directly under the skin of the back.
- To overcome the porky taste add drops of rosemary.
- Used throughout South America and the US.
5.BEEF FAT

- Beef fat is processed like that of lard, but it is not its equivalent.
- Beef fat can also be derived from fat deposits elsewhere in the animal.
- The quality of this kind of fat is judged by color and texture.
- The process of producing such fat is similar to the production of lard.
6. BACK FAT

- This is the fat that runs along the back of the pig over the loin.
- Used primarily for larding dry meats such as veal and game birds.
- Cut into strips called lardoons, fat can be inserted into the flesh using a needle to keep it soft while cooking.
7.VEAL KIDNEY FAT
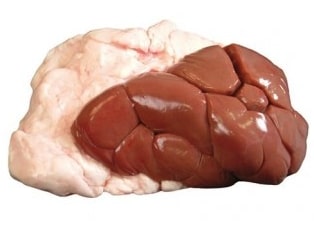
- Veal kidney fat is the leaf fat from a veal carcass.
- It is highly prized in many kitchens for its mild flavor.
- Such types of fats are normally prepared in the hotel’s kitchen due to their short supply.
8. POULTRY FAT

- Poultry fats are used in some kitchens because they have a very distinctive flavor and aroma.
- These fats are commonly available commercially and can be also made in the kitchen.
- Goose or chicken fats are commonly used in pates to enhance the favors.
- RouxRoux - Roux is flour and fat cooked together and used to thicken sauces. Roux is typically made from... from chicken fat is also commonly used in the preparation of veloute or turkey dishes.
9.DRIPPING AND GOOSE FAT

- Acquired from straining and reserving the fat that has dripped off a roasting joint or bird.
- Drippings from different kinds of meat should not be mixed.
- Beef drippings can be used to fry the beef stews.
- Drippings from goose or duck are used for bean dished, roast vegetables, fried potatoes
- Lamb drippings smell unpleasant.
10.WINTERIZED FAT

- These are fats that are winterized to ensure a certain level of saturation.
- Liquid pork or beef fat is allowed to cool slowly.
- This type of fat will have relatively little flavor or odor.
- Winterized fats can achieve high frying temperatures due to their purity.
11. SHORTENING

- Shortening is a type of fat that has additives that enhance its usage in baked or as a frying fat.
- All hard fats are shortenings.
- They are capable of producing a crumbly shortcrust.
- The white cooking fats may be made of blended vegetable oils or a mixture of vegetable and animal fats or fish oils.
- They are bland light in texture and fluffy.
- The texture of white cooking fat makes creaming and rubbing easier
- It is flavorless.
12. GHEE

- A type of clarified butter made by heating ordinary butter to get rid of impurities.
- Ghee is typically prepared by simmering butter, which is churned from cream (traditionally made by churning Dahi).
- Skimming any impurities from the surface, then pouring and retaining the clear liquid fat while discarding the solid residue that has settled to the bottom.
- Spices can be added for flavor and the texture, color, and taste of ghee depend on the quality of the butter, the milk source used in the process and the duration of time spent boiling.
13. Other most commonly used oils:

Groundnut oil, coconut oil, MustardThe three main kinds are English - strong; French -milder; and German - spiced with herbs. also coar... oil, Soybean oil, Sunflower oil, Olive oil, Corn oil, Walnut oilOne of the many kinds of oil used in salad dressings., etc. are commonly used in the hotel kitchen.
Oil varieties are available in different grades and qualities. For example, olive oil which is rich and easy to digest is sold under various grades such as:
Virgin olive oil: Mixed with other oils and from the second or third press.
Pure: Mixed virgin and refined oils.
Extra virgin: The purest oil obtained only from the first pressing.
In hotels and restaurants, various types of fats and oils are used for cooking and food preparation. The choice of fats and oils depends on the culinary requirements, flavour preferences, and nutritional considerations. Here are some common types of fats and oils used in the hospitality industry:
- Vegetable Oil:
- Soybean Oil: A versatile and neutral-flavoured oil suitable for frying, sautéing, and salad dressings.
- Canola Oil: Low in saturated fat and has a high smoke point, making it suitable for various cooking methods.
- Corn Oil: Often used for frying and baking due to its high smoke point.
- Olive Oil:
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Highest quality and most flavorful olive oil, used primarily in salad dressings and as a finishing oil.
- Virgin Olive Oil: Slightly lower quality than extra virgin but still suitable for salad dressings and cooking at lower temperatures.
- Light or Regular Olive Oil: Refined olive oil with a milder flavor, suitable for high-heat cooking.
- Animal Fats:
- Butter: Adds rich flavor to dishes and is often used in baking and sautéing.
- Clarified Butter (Ghee): Butter with the milk solids removed, providing a higher smoke point and a nutty flavor.
- Nut Oils:
- Peanut Oil: Commonly used for frying due to its high smoke point.
- Walnut Oil, Almond Oil, Hazelnut Oil: Specialty oils used for salad dressings and adding unique flavors to dishes.
- Fish Oils:
- Fish Oil: Sometimes used in certain cuisines for flavor enhancement, especially in Asian cooking.
- Specialty Oils:
- Avocado Oil: Known for its high smoke point and rich, buttery flavor; suitable for high-heat cooking.
- Coconut Oil: Often used in tropical cuisines and baking; solid at room temperature.
- Palm Oil:
- Red Palm Oil: Used in some cuisines, especially in Africa and Southeast Asia; has a distinct flavor and is rich in antioxidants.
- Canola-Olive Oil BlendBlend - To mix two or more ingredients so completely that they lose their separate identities.:
- A blend of canola and olive oil, combining the benefits of both oils.
When selecting fats and oils for cooking, chefs consider factors such as flavor, smoke point, nutritional content, and the specific cooking method. It’s common for chefs to use a combination of different oils to achieve the desired characteristics in their dishes. Additionally, there is an increasing emphasis on using healthier oils with lower saturated fat content in response to health-conscious consumer preferences.