Five Step Process In Restaurant Revenue Management Approach
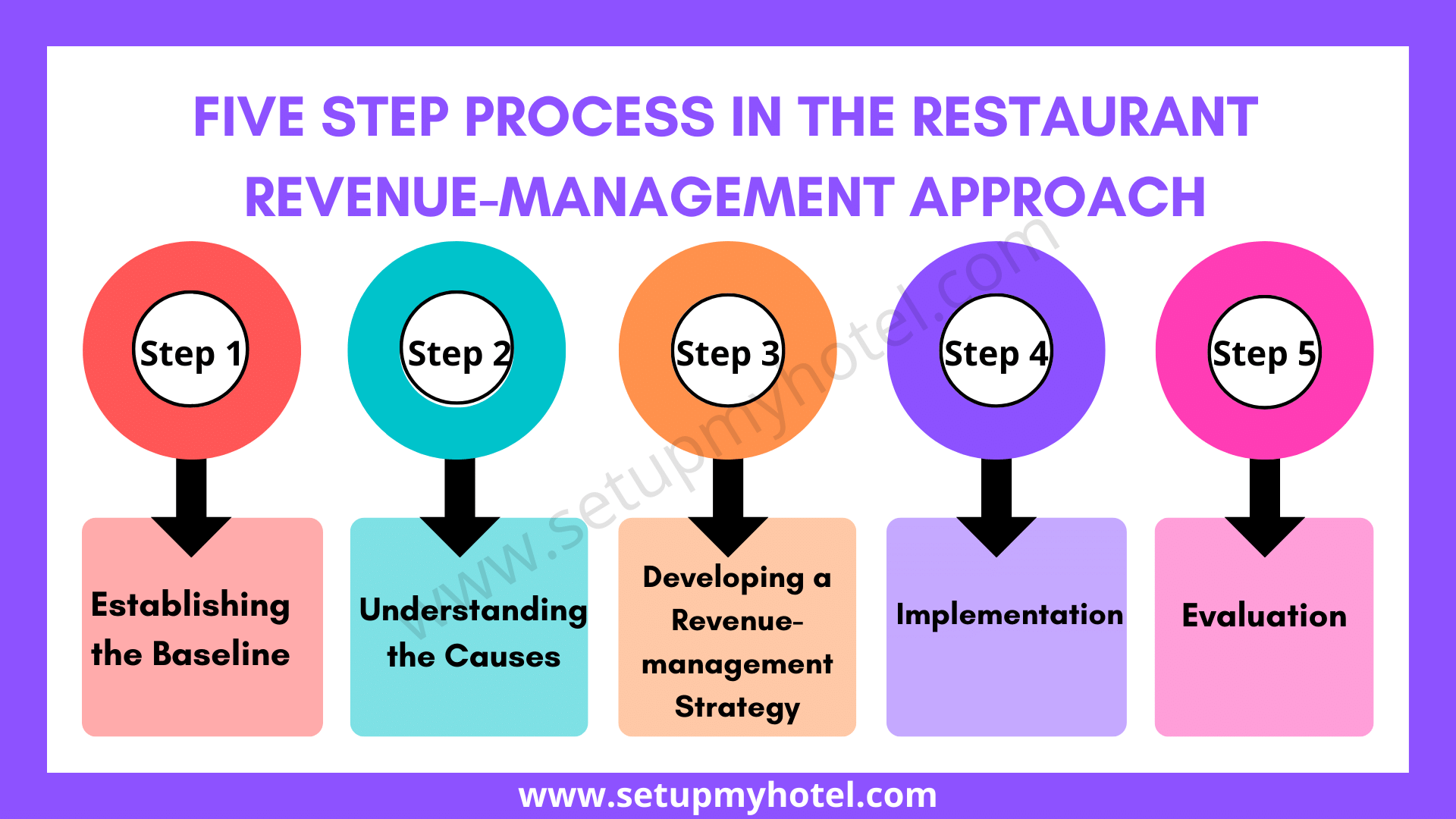
Five-Step Process In Revenue – Management Approach The five-step process outlined above was used to develop a revenue management strategy ...
Read more
Advantages Of Using Point Of Sales (POS) System In Hotels

Advantages Of Using Point Of Sales (POS) System In Hotels Introduction: Point of sale (POS) systems play an important role in ...
Read more
Main Functions And Features Of Point Of Sale (POS) System In Hotels

Functions Of Point Of Sale System In Hotels Point of Sale (POS) systems play a crucial role in the hospitality ...
Read more
History Of The Food Service Industry [Timeline]
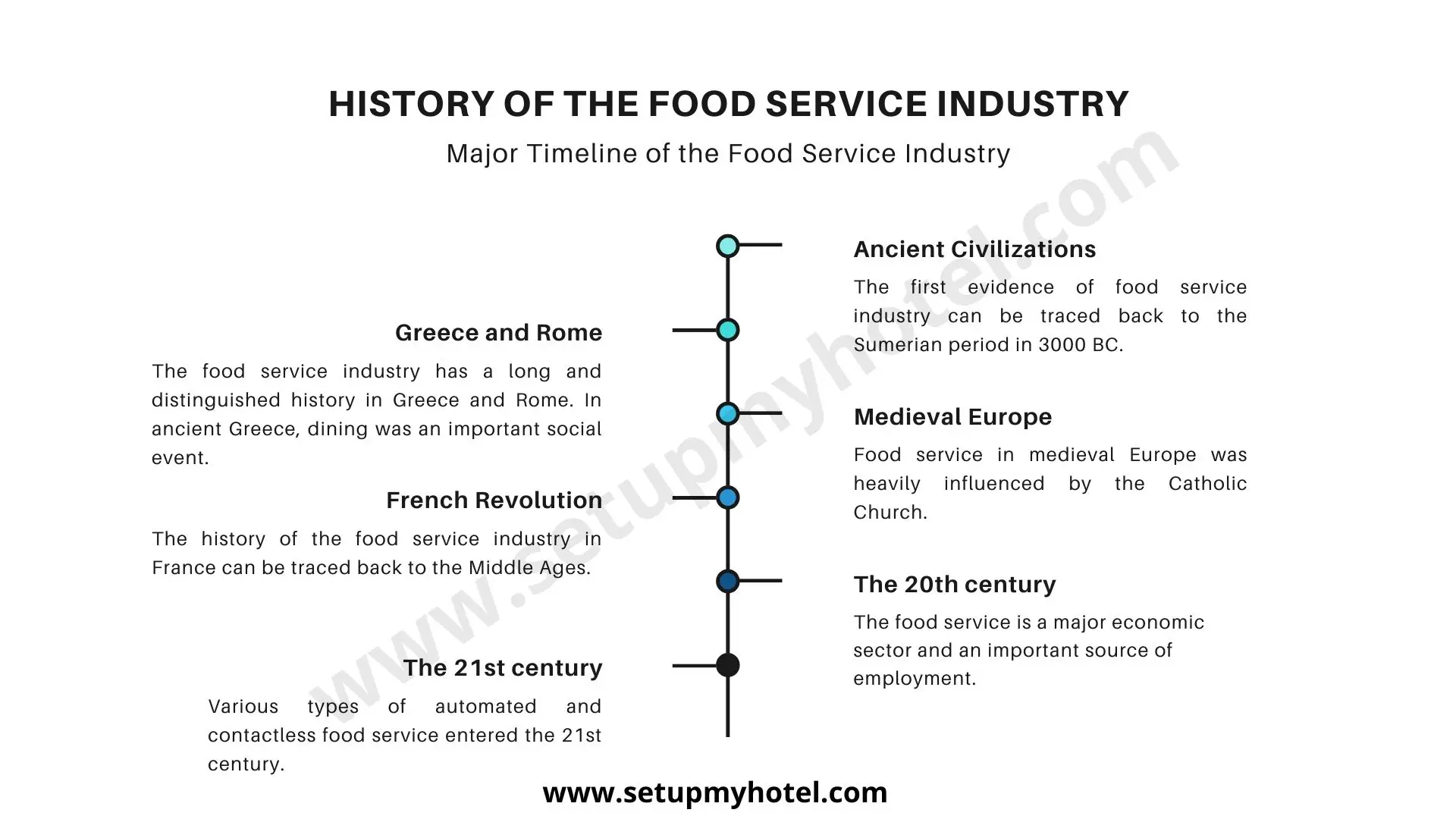
History Of The Food Service Industry The Introduction: One of the most fascinating developments in the history of food service ...
Read more
The Main Factors Of Restaurant Revenue Management
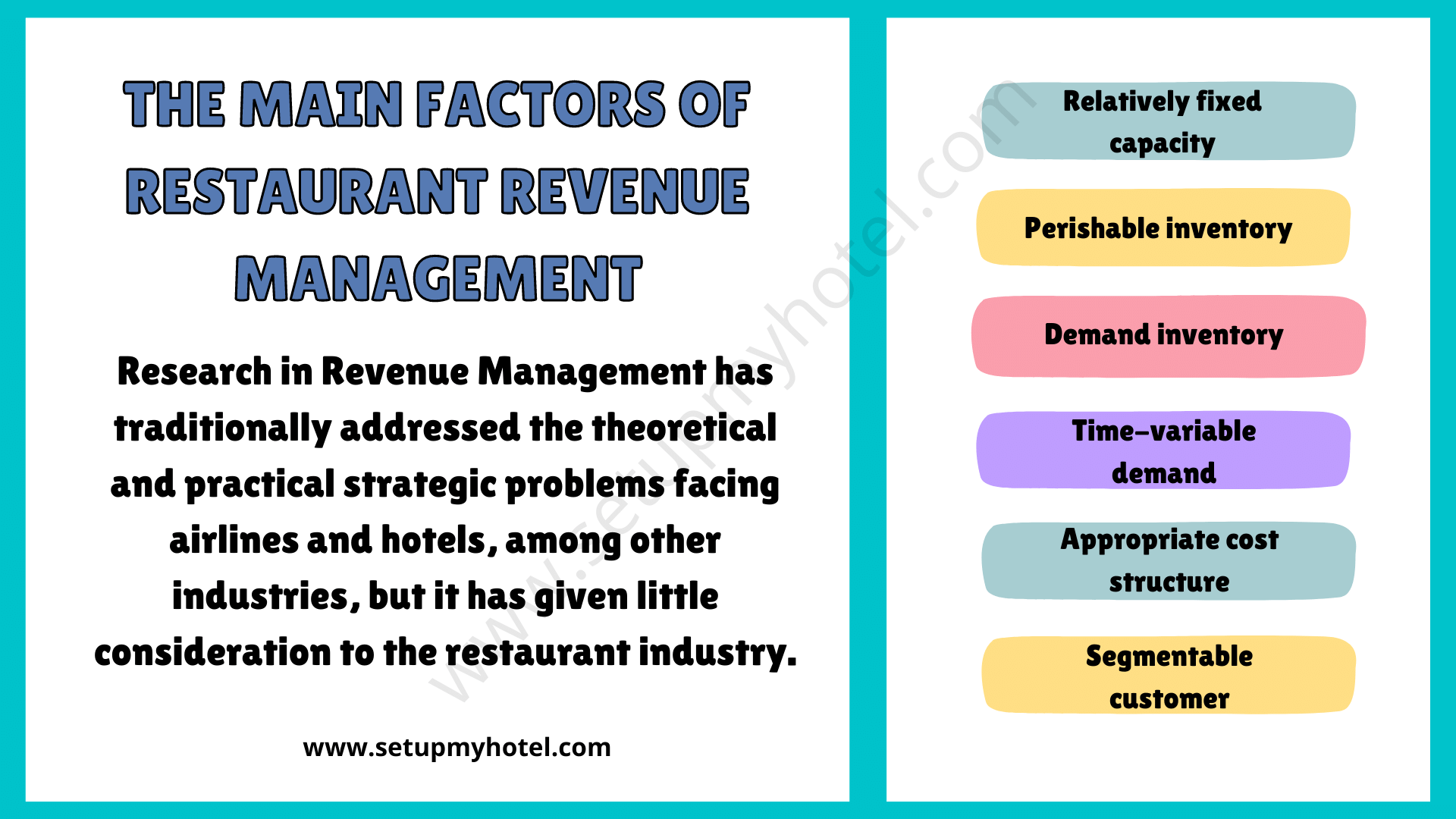
The Main Factors Of Restaurant Revenue Management Restaurant revenue management involves a strategic approach to pricing, marketing, and operations to ...
Read more
The Sequence Of Service In Restaurant (Stages Of Food Service)
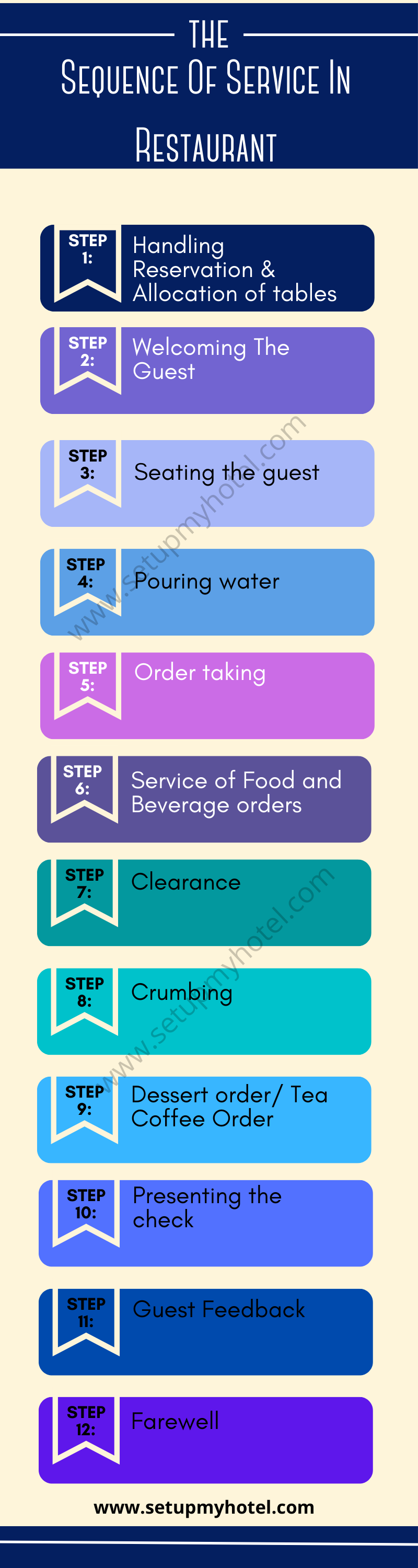
The Sequence Of Service In Restaurant The sequence of service in a restaurant is a crucial aspect of providing a ...
Read more
Top Factors That Affect How Quickly Foods Will Cool Down

Methods and Factors that help in cooling down foods quickly Foods that are too hot can be dangerous to eat. To ...
Read more